
University of Wisconsin-Madison
Master's in Computer Science
Aug 2019 - Dec 2021
GPA: 3.86/4.0
Courses: Deep Learning, Mobile & Wireless Networking, Big Data Systems, Adv. Machine Learning, Non-Linear Optimization, Adv. Computer Networks

Master's in Computer Science
Aug 2019 - Dec 2021
GPA: 3.86/4.0
Courses: Deep Learning, Mobile & Wireless Networking, Big Data Systems, Adv. Machine Learning, Non-Linear Optimization, Adv. Computer Networks

Bachelor of Technology in Electronics and Communication with minor in Computer Science
July 2015 - June 2019
GPA: 9.16/10.00
Supervisor: Prof. S. Y. Li, Dept. of CS, UW-Madison | Sep - Dec 2020
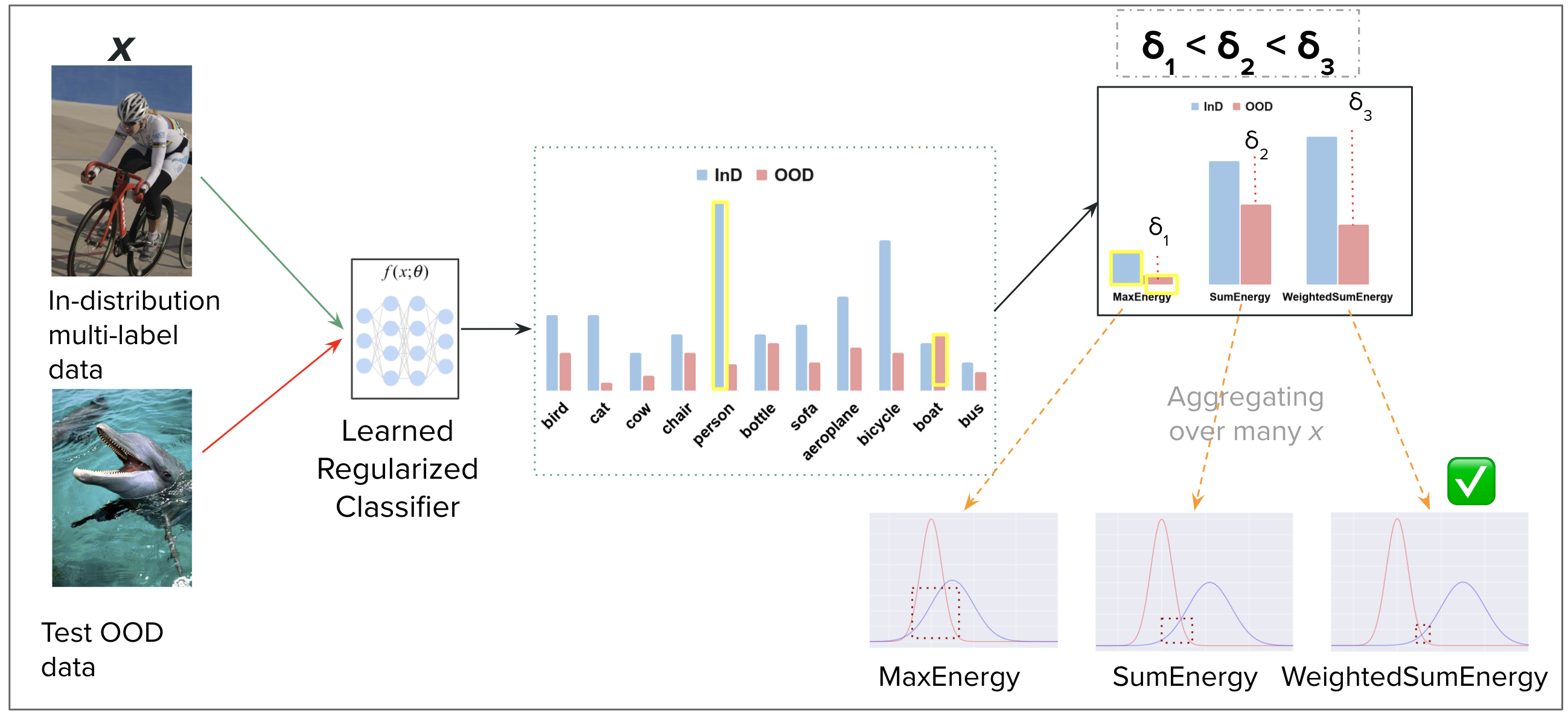
Robustness to out-of-distribution (OOD) samples during inference is an important goal in building reliable machine learning systems. OOD detection in multi-class classification have been explored significantly. On the other hand, it still remains an unexplored area in the case of multi- label classification. A recent development has shown that using SumEnergy, a method which aggregates energy scores from all the labels to obtain OOD indicator score, pro- vides significant improvement in the performance as compared to other baselines. But SumEnergy has only been applied on pre-trained networks and it naively sums energies of all the labels. We propose a new scoring function - WeightedSumEnergy (WSE), which appropriately weights the energies before summing them up. We also show theoretically that WSE is superior to SumEnergy. We propose a method (REO) for explicit regularization of energy scores on auxiliary OOD data during training time. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods on common multi-label classification benchmarks, PASCAL-VOC, COCO and NUS-WIDE with different auxiliary and test OOD datasets such as ImageNet and Texture. We show that WeightedSumEnergy reduces the FPR95 on pretrained models by 93% on an average when compared to SumEnergy, establish- ing state-of-the-art performance. We show that REO can reduce the FPR95 by up to 32.27% compared to the previous best baseline if SumEnergy is used. Moreover we get almost 0 FPR95 when WSE is used on models trained with REO, which shows the benefit of regularization.
Supervisor: Prof. S. Banerjee, Dept. of CS, UW-Madison | Sep - Dec 2020
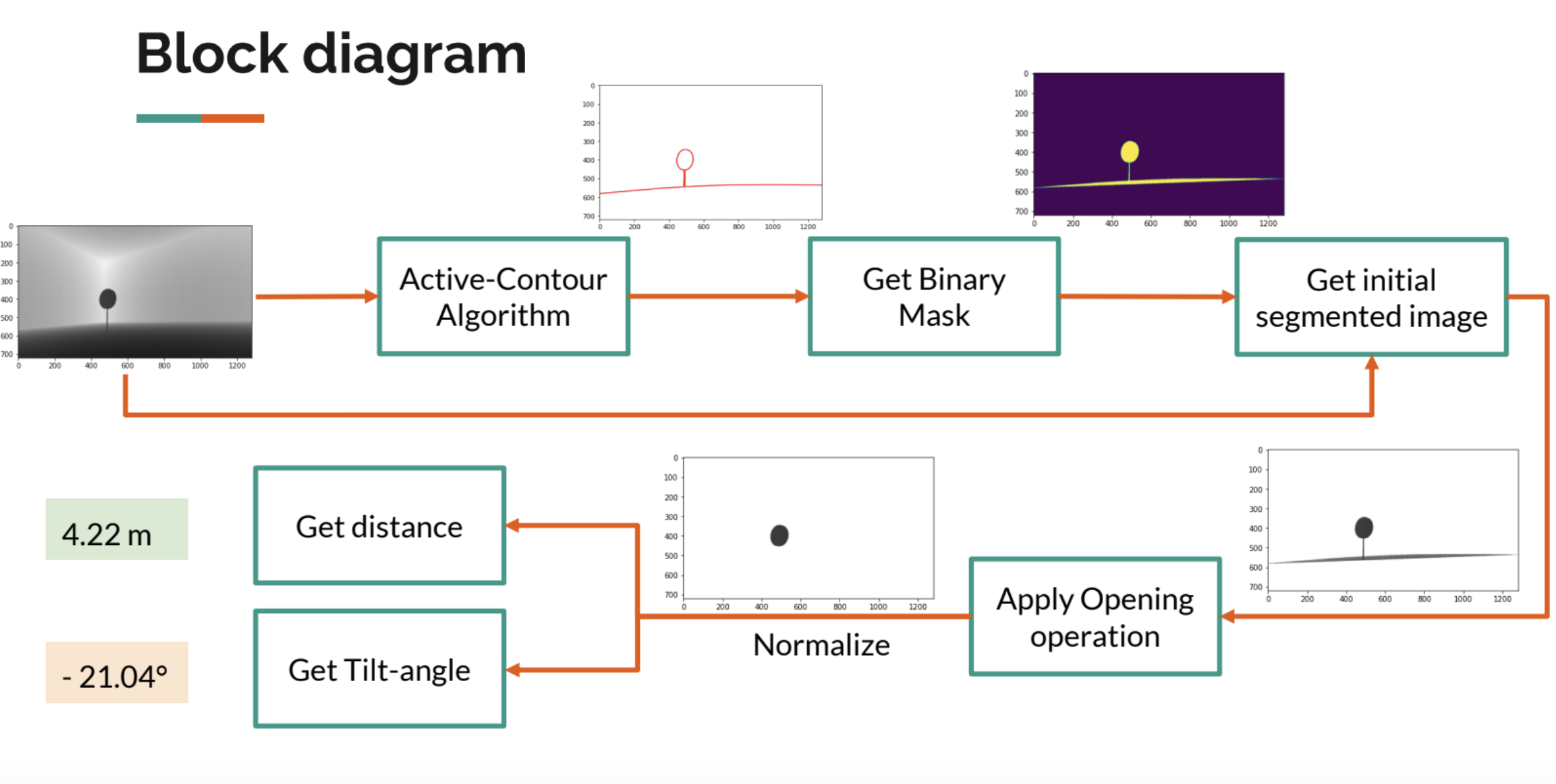
Self-driving technology presents a rare opportunity to improve the quality of life in many of our communities. Avoidable collisions, single-occupant commuters, and vehicle emissions are choking cities, while infrastructure strains under rapid urban growth. We can apply our data analysis skills to advance the state of self-driving technology. However, testing the safety and performance of real vehicles is costly and hazardous. The use of such vehicles is also outside the reach of most researchers and students. This implies technical R&D on self-driving cars has traditionally been inaccessible to the broader research community. In this course project, we help develop an open-source, affordable, and high-performance autonomous vehicle testbed. Specifically, we aim to unlock technical research and development on a higher-level autonomy perception system. The perception module interfaces and controls the various sensors including scanning LiDARs, cameras, inertial sensors, etc. The sensors provide the platform with the ability to understand its surrounding operating environment. Deployed MobileNet, a light-weighted object detecUon model for detecUng road signs on Jetson Xavier NX Developer Kit. Achieved accuracy >95% in classifying. Used efficient active-contour based image segmentaUon to get distance and angle of tilt of the road sign.
Tags: Python, OpenCV, Image Segmentation, Object Detection, CNN
Supervisor: Prof. L. Roald, Dept. of ECE, UW-Madison | Jan - Apr 2020
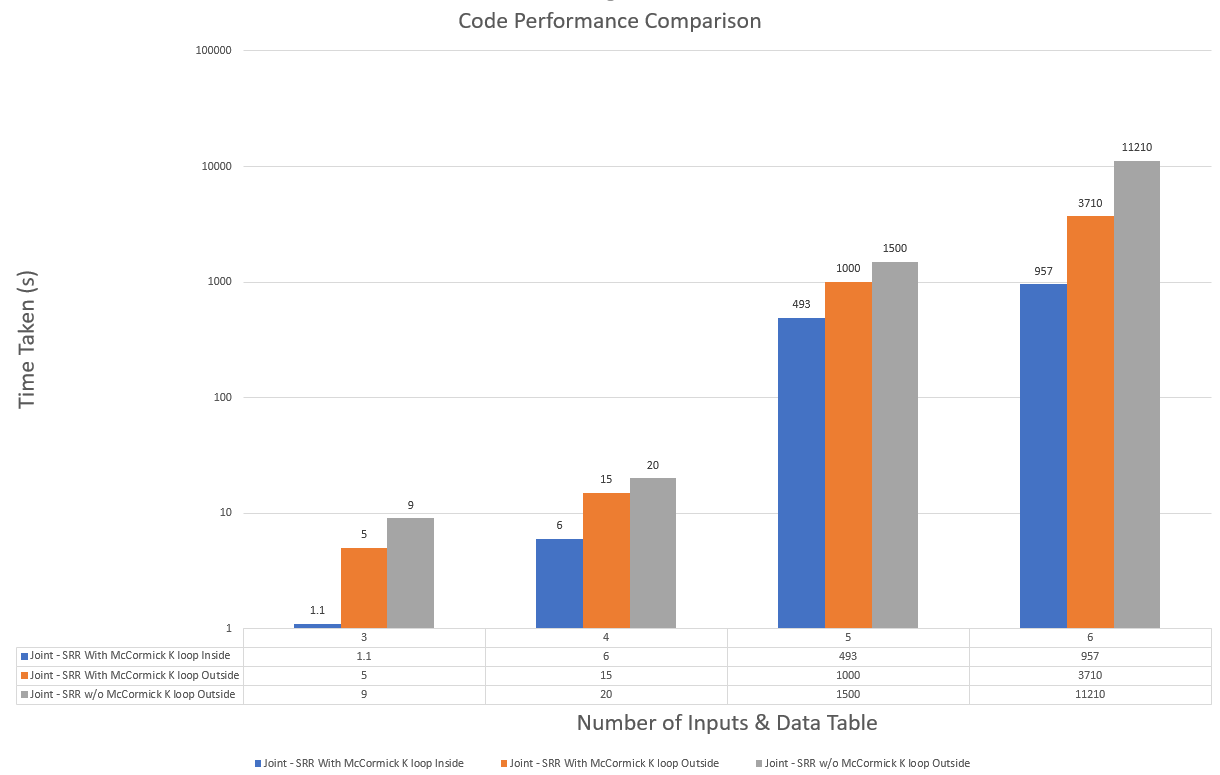
All sorts of tournament happen across the globe every year, many of which use a standard game-playing format to either help decide a winner, or for seeding in later rounds of the tournament. One of the most common and well-recognized formats used in tournaments is the round-robin tournament. This is a format in which all teams participating in the tournament play every other team once. A modification of this tournament is the double round-robin standard. This is a pretty intuitive change from the standard round-robin format, with each team playing every other team twice. The mathematical model was created for such kind of tournaments and implemented with an objective of minimizing the travel cost in the whole tournament. Two methods - Greedy and Joint optimization based were implemented and analyzed.
Supervisor: Prof. A. Akella, Dept. of CS, UW-Madison | Jan - Apr 2020
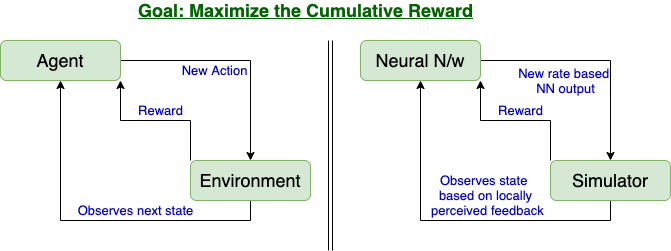
Congestion control schemes are significant in determining throughput and latency of data center networking. Several schemes have been proposed to meet the growing demands of data centers’ applications. While DCQCN is being used in Microsoft, TIMELY is deployed in Google’s data centers. HPCC is found to be more effective than the ones which are currently deployed. It is currently being deployed at Alibaba. Apart from these, machine learning techniques are also being explored in this area. While DCECN uses GMM-based classifier to identify and prioritize flow to prevent congestion, Aurora uses Reinforcement Learning (RL) to change the congestion rate. Taurus introduces the idea of intelligent data-plane which not only can be used in congestion control, but other applications as well like packet anomaly detection. The paper aims to discuss these different protocols in brief, including the key ideas and architecture. Advantages and limitations are also described to give the reader knowledge in a nutshell.
Supervisor: Prof. P. K. Bora, Dept. of EEE, IITG | Aug 2018 - Apr 2019
With the rise of cameras and smart phones the number of images is growing exponentially. Along with that, with an advent of digital manipulation tools, it has now become very easy to do image forgery. Resampling is one of the important characteristic of forged images. In this project, classifiers for detecting image forgery using convolutional neural network were implemented, followed by localization algorithm. CNN with a prediction error layer is used to classify a patch of an image as resampled or original. Resampling could be of different types. 4 types of resampling were considered which are usually involved in image forgery. These are: upscaling, downscaling, clockwise rotation, counter-clockwise rotation. Image processing features like Gaussian blurring, and median blurring are also included. After classifying using 6 classifiers, 6 probability maps are obtained. Localization is done based on the assumption that forged probability map will have a bimodal distribution. Bilateral filtering, followed by random walker segmentation and binarization method by Otsu are used to obtain the final mask image. Achieved accuracy of 96% and F1 score > 99.5%. Also, the mask closely matches with the ground truth mask of the forged image.
Tags: Python, Tensorflow, Keras, Numpy, Computer Vision, Machine Learning, Image Processing
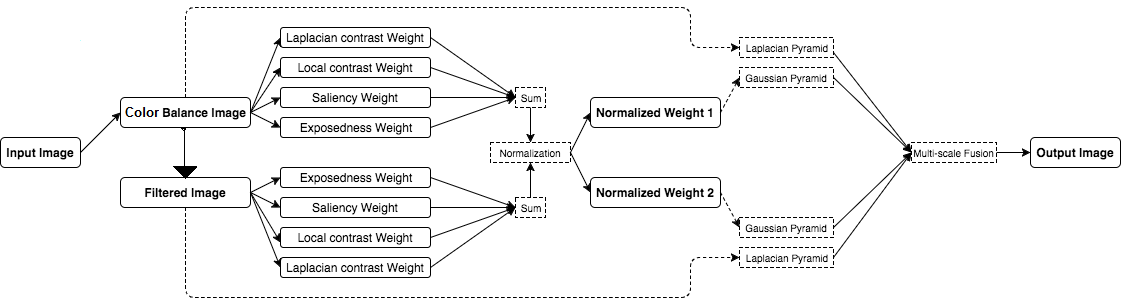
Supervisor: Prof. P. Guha, Dept. of EEE, IITG | Aug 2017 - Nov 2017
Built on the fusion principles, the strategy derives the inputs and the weight measures only from the degraded version of the image. In order to overcome the limitations of the underwater medium two inputs were defined that represent color corrected and contrast enhanced versions of the original underwater image, and also four weight maps that aim to increase the visibility of the distant objects degraded due to the medium scattering and absorption. The strategy is a single image approach that does not require specialized hardware or knowledge about the underwater conditions or scene structure. The fusion framework also supports temporal coherence between adjacent frames by performing an effective edge preserving noise reduction strategy. The enhanced images are characterized by reduced noise level, better exposedness of the dark regions, improved global contrast while the finest details and edges are enhanced significantly. Experimental validity of the method is done by qualitative and quantitative analysis on several images using image quality index -- Entropy and Contrast Improvement Index (CII).
Tags: MATLAB, OpenCV, Image Processing, Digital Signal Processing
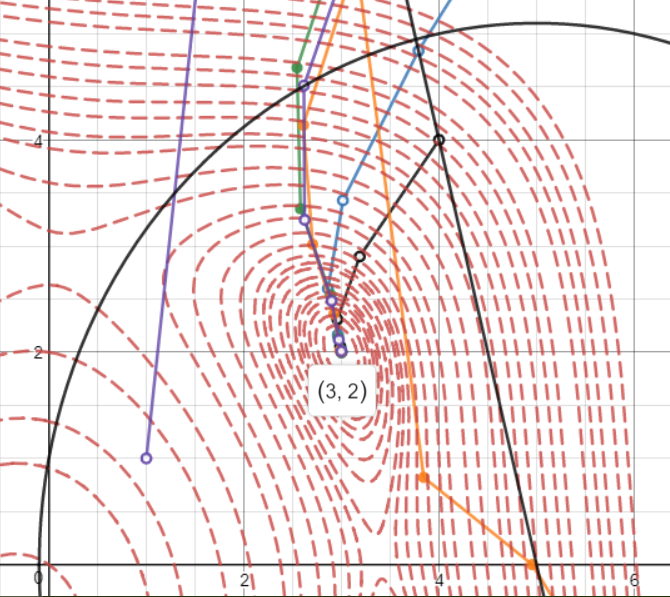
Supervisor: Prof. D. Sharma, Dept. of ME, IITG | Aug 2018 - Nov 2018
Real world non-linear problems with non-linear constraints are solved using sequential quadratic programming algorithm, developed from scratch. Firstly, the non-linearity is reduced to quadratic form using taylor-series approximation. Karush Kuhn Tucker (KKT) conditions are then used to convert a quadratic constraint optimization problem into a linear problem. The conditioned simplex method is used to solve the linear programming problem (LPP).
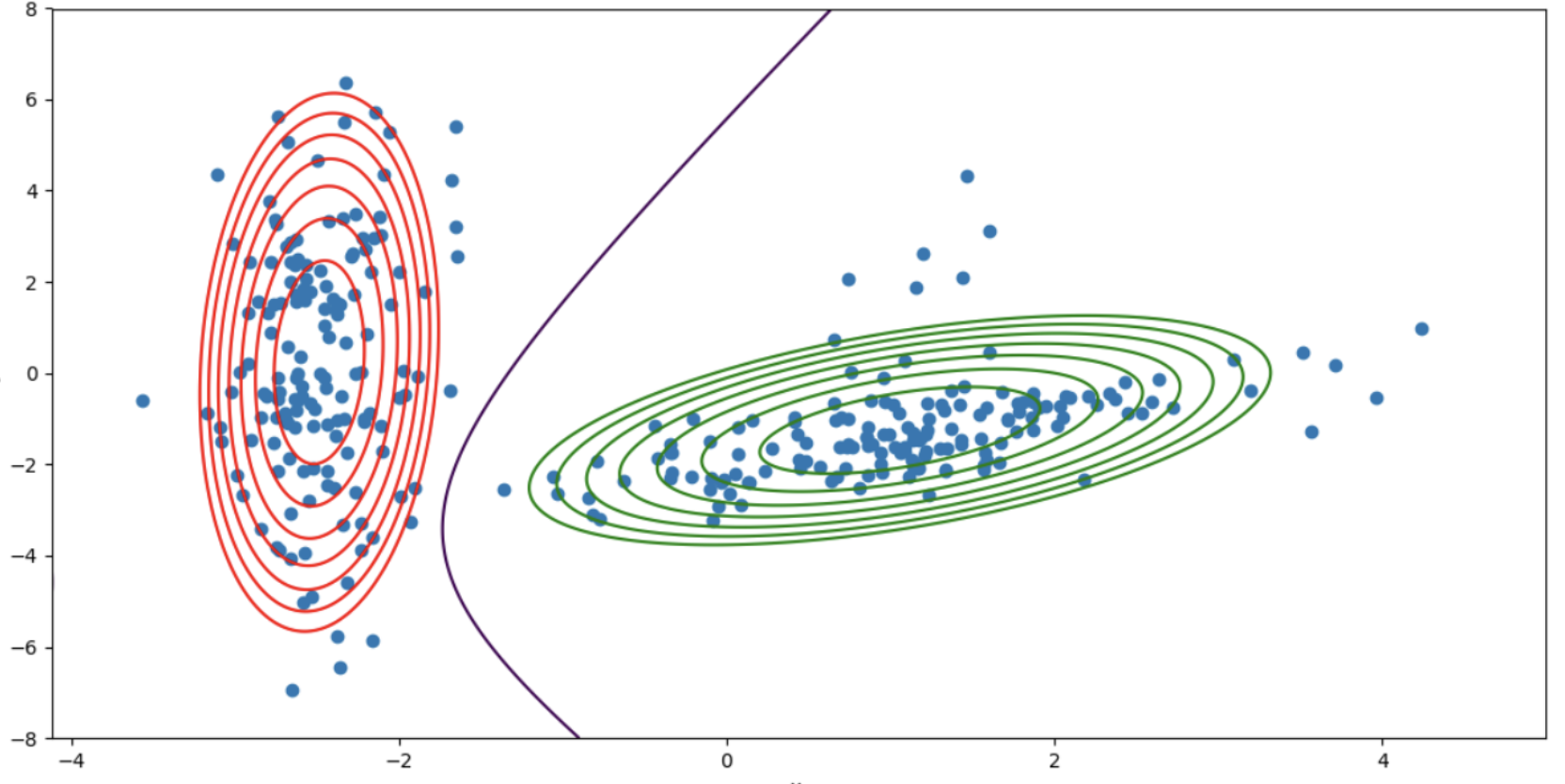
Supervisor: Prof. T. Jacob, Dept. of EEE, IITG | Jan 2018 - Apr 2018
Multivariate Regression:Wage dataset having income survey information of a group of males from Atlantic region of the United States, was used to determine the relationship between different attributes using multivariate polynomial regression from scratch. Decision Trees: Wisconsin Diagnostic Breast Cancer (WDBC) dataset from the UCI repository was used for classification of samples of biopsied tissue as malignant and benign. Achieved accuracy of 94.73%.
Tags: Python, Keras, Machine Learning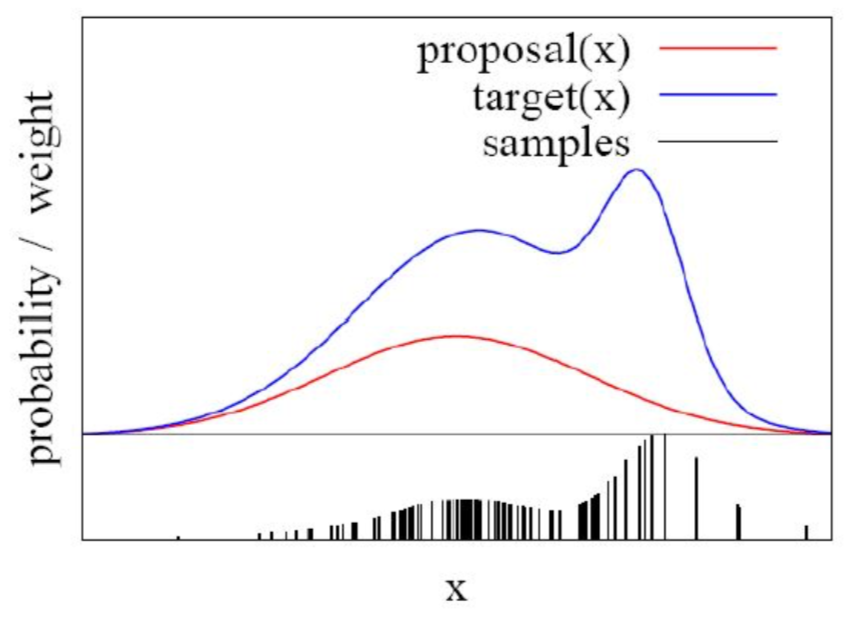
Supervisor: Prof. M. K. Bhuyan, Dept. of EEE, IITG | Jan - Apr 2019
Particle filters are based on probabilistic representations of states by a set of samples (particles), with the advantage of making possible the representation of non-linear system and measurement models, and multi-modal non-Gaussian density states. The key idea of particle filters is to represent and maintain the posteriori density function by a set of random samples with associated weights and to compute the state estimate from those samples and those weights. As the number of samples becomes very large, this characterization becomes an equivalent representation to the usual function description of the posteriori probability density function (PDF), and the method approaches the optimal Bayesian estimate. Particle Filter is a hypothesis tracker, that approximates the filtered posterior distribution by a set of weighted particles. It weights particles based on a likelihood/correlation score and then propagates these particles according to a motion model.
Tags: Python, OpenCV, Computer Vision, Image Processing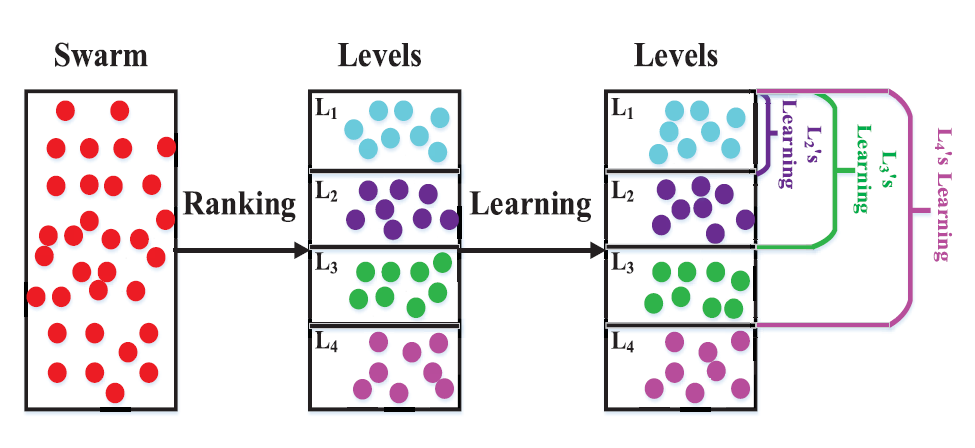
Supervisor: Prof. G. Trivedi, Dept. of EEE, IITG | Jan - Apr 2019
In instructional method used in pedagogy, instructors normally divides mixed-level students into different levels, and instruct/teach them as per their intellectual and learning capacities. Roused from this thought, particles are considered as mixed level students. A level based learning swarm optimizer (LLSO) settles substantial scale optimization. At initial, a level-based learning technique is presented, which isolates particles into various levels as indicated by their fitness-values and treats particles in various levels in a distinct way. At that point, another model determination methodology called exemplar selection strategy is intended to randomly choose two predominant particles from two different higher levels in the current swarm to control the learning of particles. The collaboration between these two methodologies results in improvement for the optimizer. In this project, LLSO was implemented as a sequential code and using OpenMP as a parallel code. Parallel code is found to be run faster than the sequential code. The results were compiled using IITG’s super computer - PARAM-ISHAN.
Tags: C++, OpenMP, Parallel Computing, Optimization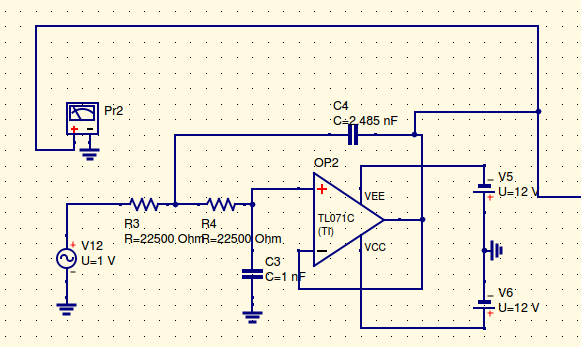
Supervisor: Prof. M. Arrawatia, Dept. of EEE, IITG | Jan - Apr 2018
This project focuses on active low-pass filter design using operational amplifiers. Particularly, interested in designing a low-sensitivity 7th order Chebyshev filter using Sallen-Key topology. Low-pass filters are commonly used to implement antialias filters in data-acquisition systems. The project discusses the Sallen-Key architecture and in brief, about Integrator Biquad. It gives a general overview and derivation of the transfer function, followed by detailed discussions of low-pass filters, including design information, and ideal and non-ideal operation. Detailed analysis of sensitivity is done considering 2nd order Chebyshev filter. The 7th order filter in designed with various stages, each having its own Q value. Also, various design challenges are tried to be addressed. The component selection is discussed too. Finally, the simulation results and in-lab experimental results are shown.
Tags: Analog Circuit Design, Active Filters